
Compliance with TCFD proposal TCFD
Endorsement of TCFD
The DCM Group deems dealing with climate change to be a materiality in its business strategy, and announced its endorsement of the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) in April 2023. Going forward, we shall disclose information in accordance with the framework promoted by the TCFD (governance, strategy, risk management, metrics and targets), and contribute to the achievement of a decarbonized society through initiatives to tackle climate change.

About TCFD
After the Paris Agreement was ratified in 2015, the world saw a movement, particularly in the financial industry, to evaluate the impact of climate change on the business activities of businesses in which funds had been invested. Against the backdrop of such a movement, Financial Stability Board formed the TCFD on the basis of a request from the G20 in order to consider the disclosure of climate-related information and the type of action financial institutions should take. The TCFD recommends companies and organization disclose information in four areas concerning climate change-related risks and opportunities: governance, strategy, risk management, and metrics and targets.
*TCFD: Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures
Governance
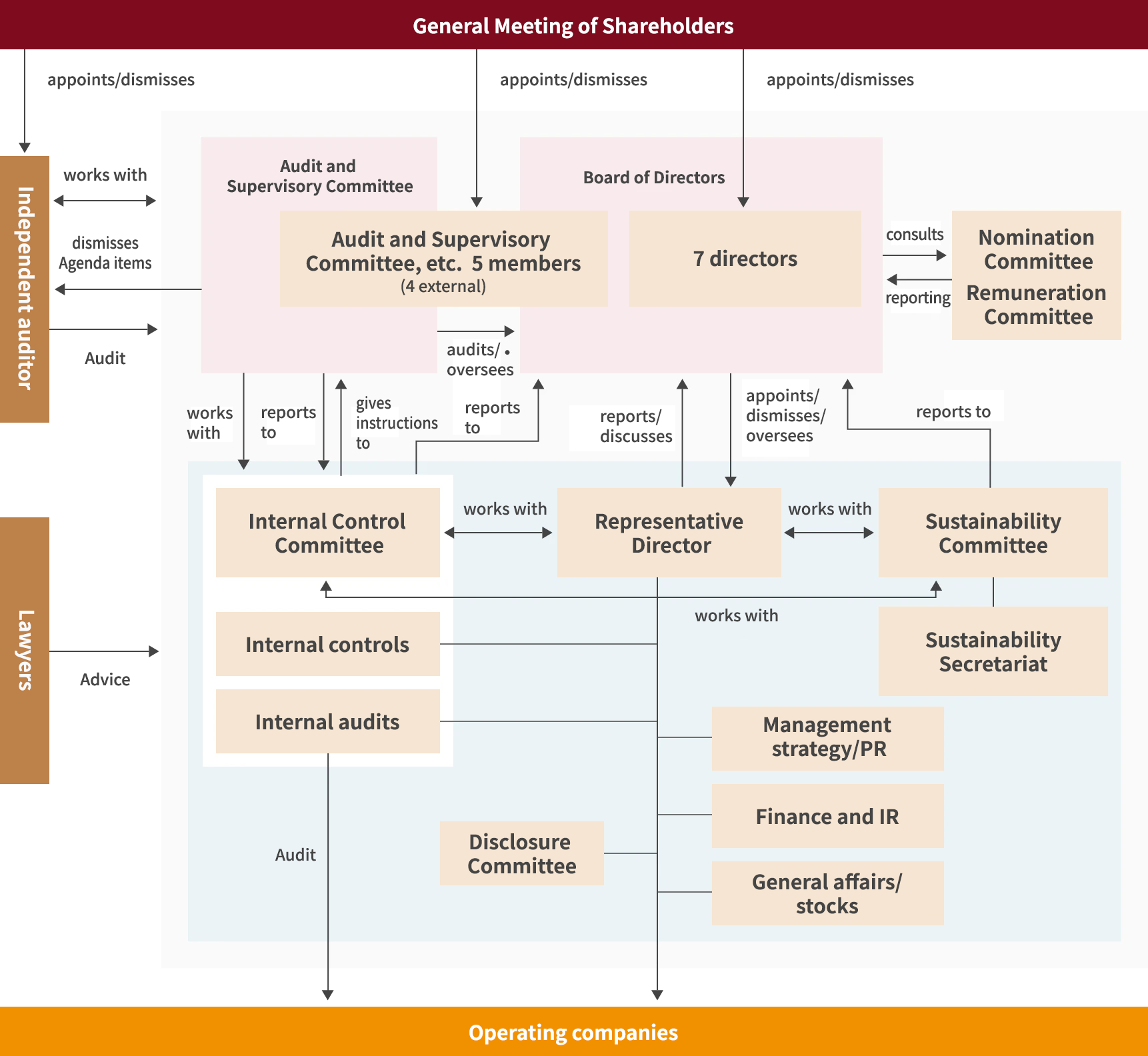
DCM considers the issue of climate change to be one of great importance concerning sustainability, and has put in place a governance structure centering on oversight of the Board of Directors and a Sustainability Committee.
The Board of Directors receives a report from the Sustainability Committee at least once a year regarding the issue of climate change and sustainability initiatives, including SDG materialities, and reviews policy and initiatives as appropriate, as well as monitoring and evaluating progress.
The Sustainability Committee is chaired by the President & CEO of DCM, and meets at least twice a year with the presence of committee members that include the director responsible for sustainability and the officer in charge of SDG materialities. The Sustainability Committee undertakes discussions concerning the issue of climate change as well as surveys, research, and progress checks for the latest movements concerning sustainability, and deliberates policy for initiatives as well as providing reports and proposals to the Board of Directors.
Governance structure
Strategy
DCM clearly identifies the long-term risks and opportunities presented by climate change, and performs scenario analysis for the creation of business strategy proposals in order to minimize risks and maximize opportunities.
In light of the fact that the target of limiting the increase in average global temperatures to 1.5℃ above pre-industrial levels as set out in the outcome document of COP26 (26th Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change) held from October to November 2021 has become mainstream around the world, we DCM has undertaken to perform analysis premised on the 1.5℃ target.
Specifically, in reference to materials such as reports on predictions issued by governments and international institutions, including scenarios RCP8.5/RCP2.6 from the IPCC and ZE2050/SDS/STEPS from the IEA’s World Energy Outlook 2021 along with other scenarios, we set out the two scenarios of decarbonization (average temperature increase of 1.5℃ to 2℃) and continued heating (average temperature increase of 2.7℃ to 4℃) and analyzed the transition risks (policy, legal, market, and reputation) and physical risks (acute, chronic) caused by climate change as well as the opportunities presented by appropriate action to deal with climate change (products and services, markets, resilience).
*IPCC: Intergovernmental Panel on Climatic Change
RCP: Representative Concentration Pathway of greenhouse gases
IEA: International Energy Agency
NZE: Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario (1.5℃)
SDS: Sustainable Development Scenario
STEPS: Stated Policies Scenario
Scenario analysis
The TCFD envisages the following two types of risk caused by climate change.
(1) Transition risk caused by policy, legal, market, and reputation changes, etc.
(2) Physical risk of damage to assets caused by intensifying abnormal weather
The DCM Group performed its investigation with a focus on the impact of transition risk in the 2℃ (or 1.5℃) scenario, and of physical risk in the 4℃ scenario.
Climate change is expected to bring a heightened environmental awareness and lifestyle changes among consumers, and it is envisaged that this will present opportunities for promotion to customers given the characteristics of the DCM Group’s business.
Premises
| Period | FY2020 to 2050 |
| Scope | All offices/branches and all businesses possessed by the DCM Group as of FY2020 |
| Calculation conditions |
・Published climate change scenarios (IPCC/IEA, etc.) used.
・Items to be included in qualitative analysis selected at a meeting of the relevant persons from involved departments. ・For risks, we mainly investigated the increased costs that will result when a risk materializes. ・For opportunities, we mainly investigated the increase in sales that will result when an opportunity materializes. ・No consideration is given to the future impact from creation of energy, road transport, and other infrastructure. |
Scenario analysis
We analyzed the impact of climate change risks and opportunities on business and indicated the magnitude of this impact using arrows. We have defined measures to address these issues by linking them to the SDG materialities, and we will also address climate change as part of sustainability management at DCM.
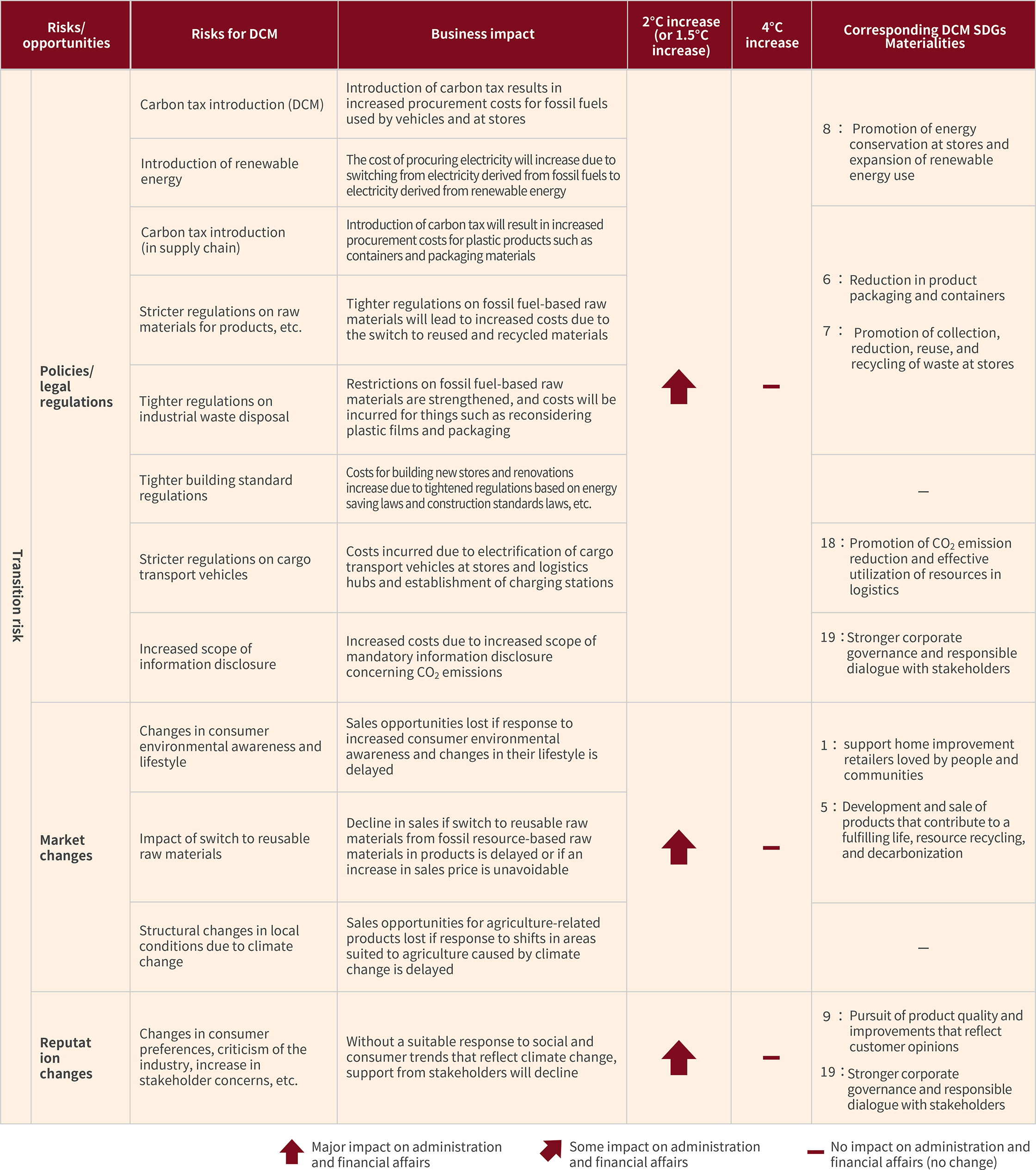
Transition risk
For transition risks, a range of policies and legal regulations have been brought in towards the 1.5℃ target, and we conducted our investigation with a focus on the decarbonization scenario (1.5℃ to 2℃ temperature increase) in which market and reputation changes occur.
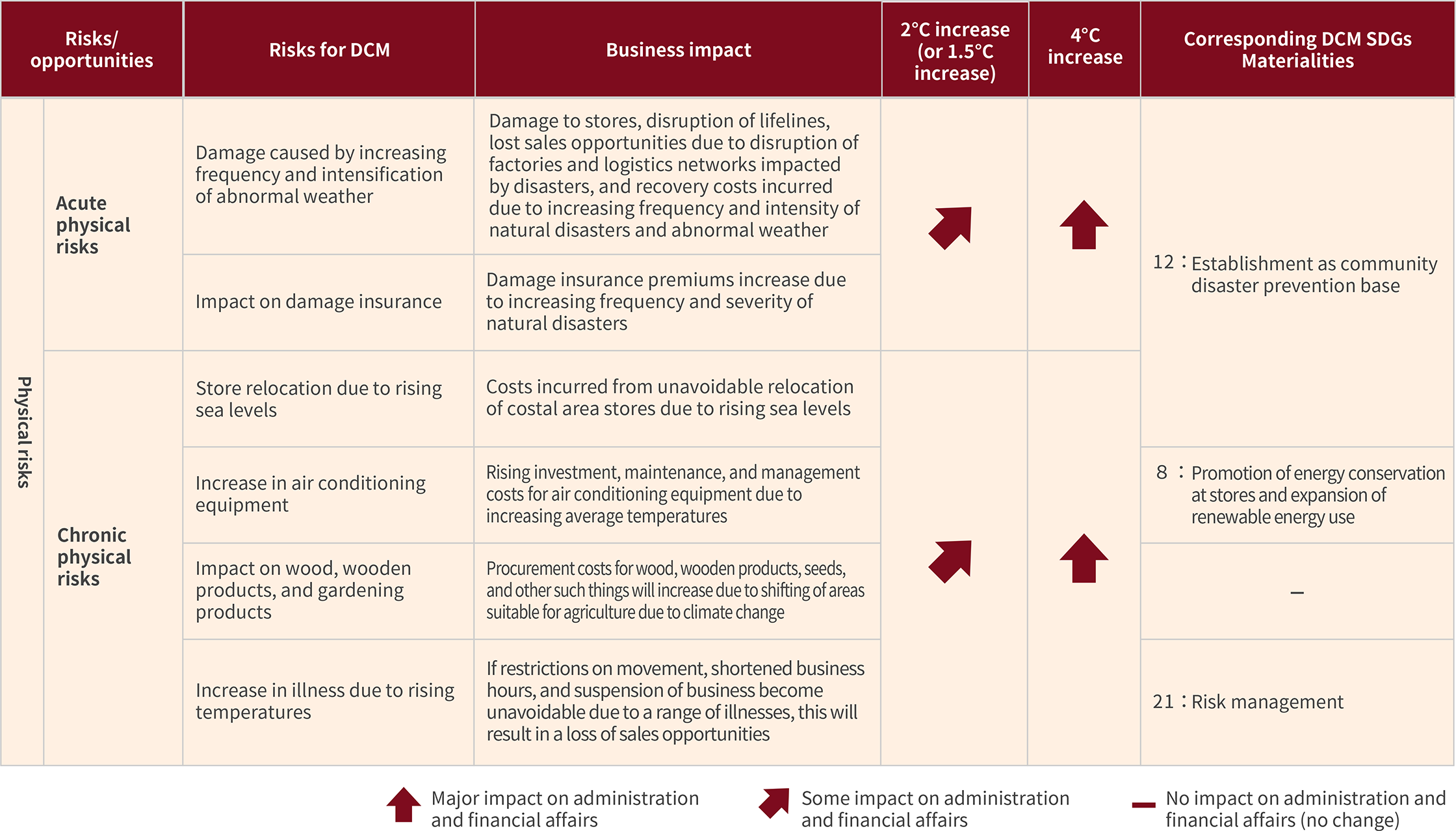
Physical risks
For physical risk, we considered the impact of extreme weather events such as heavy rains that cause disasters resulting from continued heating based on the decarbonization scenario (1.5℃ to 2℃ temperature rise). In the scenario with continued heating (2.7℃ to 4℃ temperature rise), we considered not only the impact on store locations and facilities due to rising temperatures but also the impact on DCM caused by damage to forests, agriculture, and other such things, as well as the impact of a range of infectious diseases on business, among other impacts.
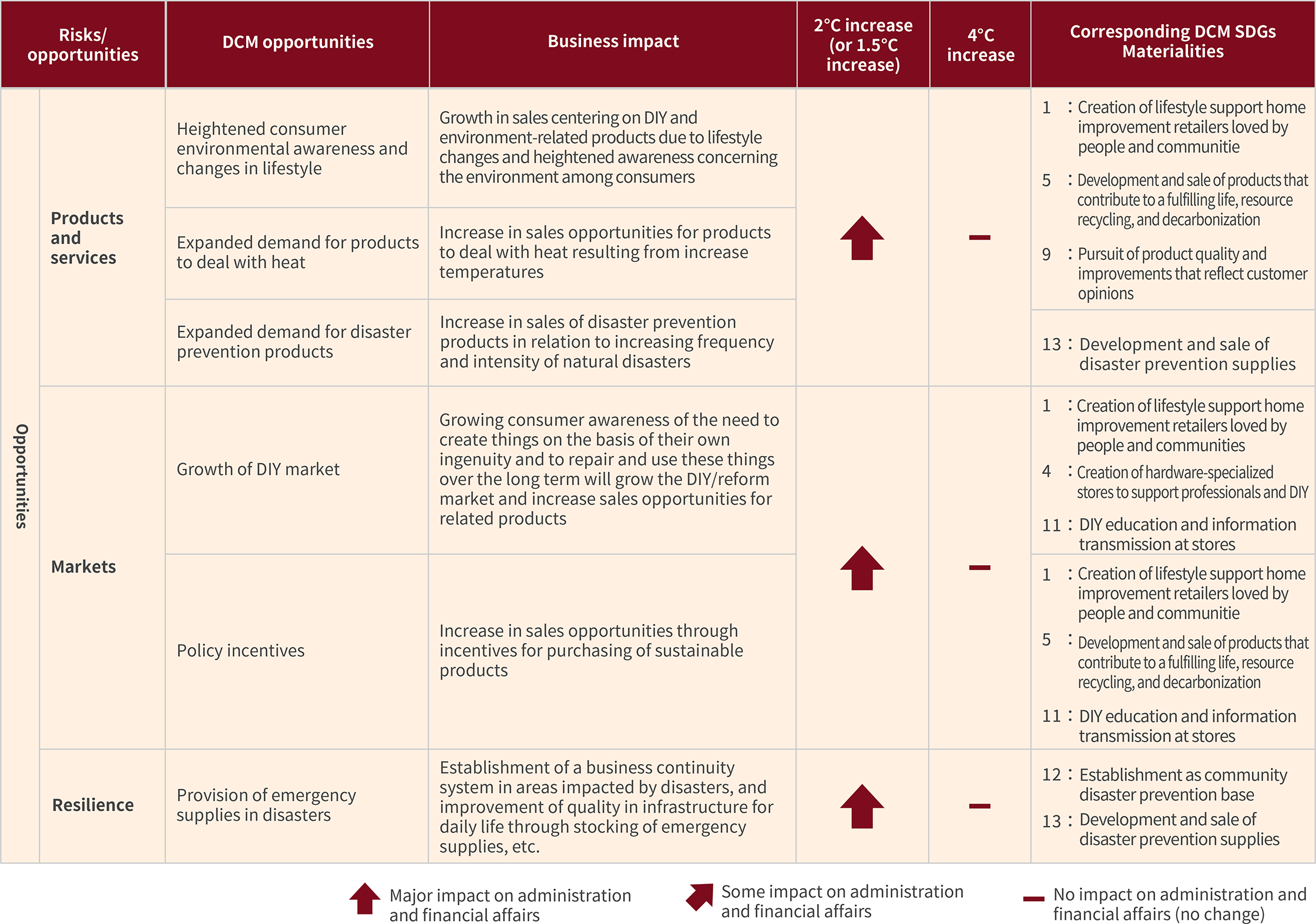
Opportunities
With regard to opportunities, in the scenario of a 1.5℃ to 2℃ temperature increase, there will be growth in demand for products to deal with heat and for disaster prevention products due to a heightening of environmental awareness among consumers and increased resonance with the approach of repairing things and taking care in the use of resources, so we envisaged that not only will sales of DIY and environment-related products grow, but also that DIY and the reform market that play a central role for home improvement retailers will grow.
Risk management
Risk management process
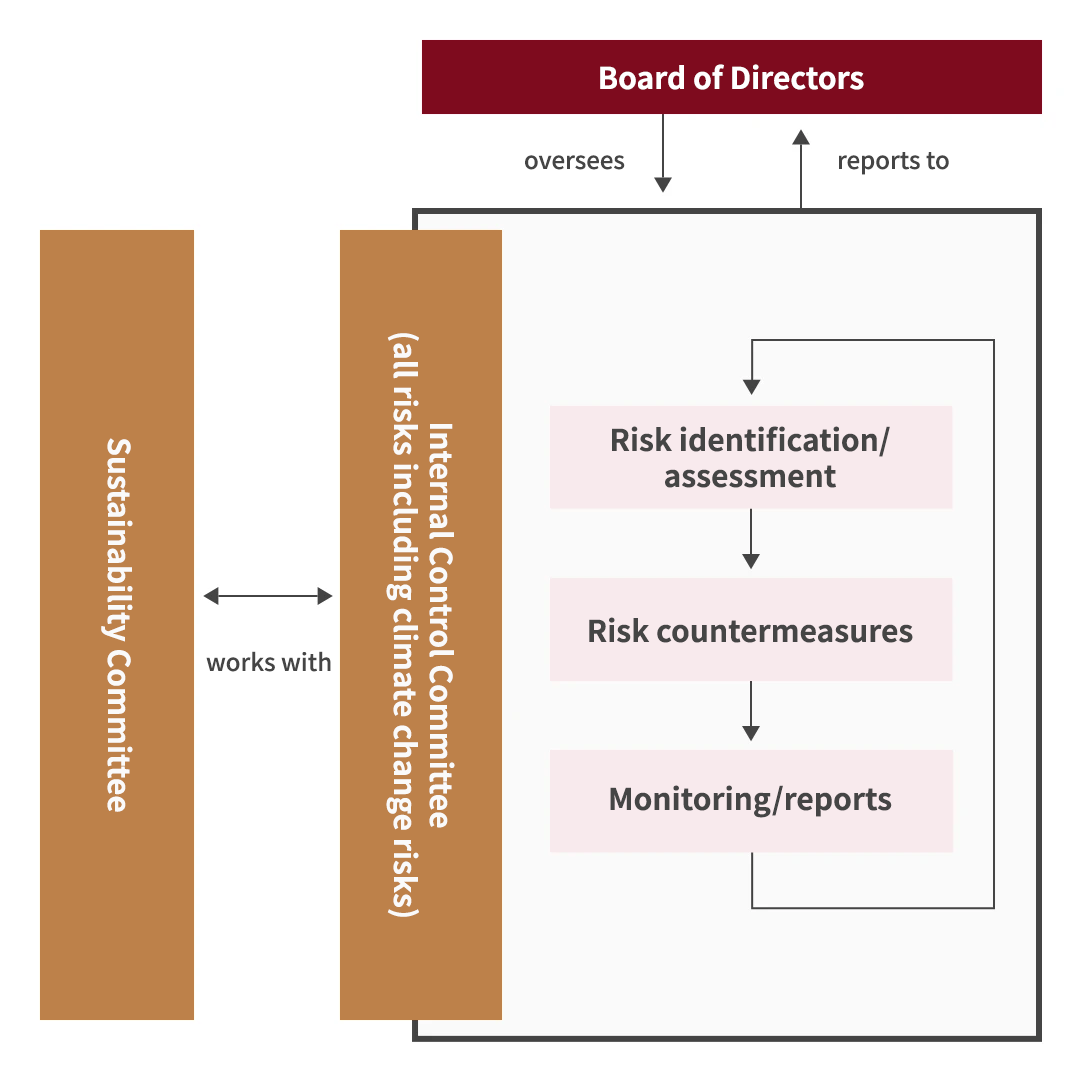
On the basis of our risk management rules, our Internal Control Committee exhaustively and comprehensively manages risk for the group as a whole, and we provide awareness raising, guidance, and education among other things in order to minimize risks and potential damage. We also manage climate change risk under this risk management system.
Each department identifies risks every year, and assesses them in consideration of their impact and frequency of occurrence. They then compile them into a risk assessment table along with countermeasures, and submit this to the Internal Control Committee. This risk assessment table also includes climate change risk. On the basis of the risk assessments and countermeasures submitted by each department, the Internal Control Committee gains a comprehensive understanding of the risk situation for the group as a whole.
For major risks that the group as a whole faces, the committee undertakes a comprehensive assessment including aspects such as details of the risk, impact in the event of materialization, and frequency of occurrence, and makes decisions on risk avoidance, mitigation, transfer, and acceptance.
Regarding this risk management status and judgments on major risks, the Internal Control Committee issues reports to and shares information with the Sustainability Committee, and each year reports to the Board of Directors, which undertakes deliberations and provides oversight. After deliberations by the Board of Directors, the Internal Control Committee undertakes monitoring of the risk management system and countermeasures on an ongoing basis.
Metrics and targets
The outcome document for COP 26 that was held between October and November 2021 states that efforts should be made to keep temperature rises to 1.5℃ above pre-industrial levels. Aiming to achieve this 1.5℃ target has become mainstream around the world, and a responsibility that companies are expected to fulfill. In the long-term scenario analysis we implemented here, the significance of the impact of climate change on government policy, legal systems, and markets, and of the impact on business of damage and other problems caused by abnormal weather became apparent. In order to prevent the growth of risk due to climate change, the DCM Group will do its utmost to help limit temperature rises to 1.5℃.
Scope 1 and 2 emissions
These were calculated in line with GHG Protocol Guidelines for all DCM Group offices and branches.
| Scope 1 (direct emissions) | 12,057 t |
| Scope 2 (indirect emissions) | 96,752 t |
| Scope 1 + 2 (total) | 108,809 t |
Scope 1 and 2 reduction target
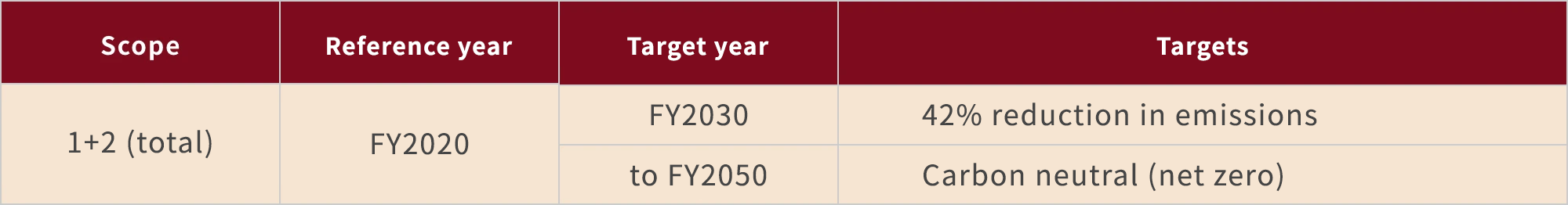
For Scope 3, we will work to increase calculation accuracy and look into reductions in collaboration with our business partners.
The DCM Group will create new products and services for our customers, flexibly respond to change, unite with the community, and achieve the form of an indispensable company that contributes to the achievement of a world that meets the target of limiting average temperature rise to 1.5℃ and serves society.

